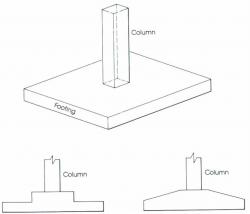
Footings are structural members used to support columns and walls and to transmit and distribute their loads to the soil in such a way that the load bearing capacity of the soil is not exceeded, excessive settlement, differential settlement, or rotation are prevented and adequate safety against overturning or sliding is maintained.
Types of Foundation
1. Shallows Foundations
2. Deep Foundations
1- Shallows Foundations
Shallow foundations are those founded near to the finished ground surface; generally where the founding depth (Df) is less than the width of the footing and less than 3m. These are not strict rules, but merely guidelines: basically, if surface loading or other surface conditions will affect the bearing capacity of a foundation it is 'shallow'
Shallows foundations are used when surface soils are sufficiently strong and stiff to support the imposed loads; they are generally unsuitable in weak or highly compressible soils, such as poorly-compacted fill, peat, recent lacustrine and alluvial deposits, etc.
Shallow Foundation Types
1. Pad or column footings ( Isolated or Combined )
A-Isolated
used to support single columns. This is one of the most economical types of footings and is used when columns are spaced at relatively long distances